Have you ever experienced that small electric shock as you touch a metal doorknob? How about hairs sticking on to a balloon?
That, my friend, is known as ESD or Electrostatic Discharge.
What is ESD?
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) usually occurs in a number of day-to-day situations.
If you try to remember, the electric shock that you experienced as you touch a metal doorknob usually happens after you happen to rub your plastic-soled shoes on a carpet.
You’re actually building up negative electrical charges (through the process of tribocharging) the whole time you’re walking on a carpet. The negative charges that are being carried are then distributed to your body or the entire surface of the object.
When you get in touch with another conductive body or object that is ground, the transfer of charges happens in a form of spark that you can actually see, hear, and feel, depending on the volts involved.
How Does ESD Damage Your Components?
Modern technology and must-have electronic devices in 2018 have evolved to be more and more sensitive to ESD damages.
Although the charge that you feel as you touch the metal doorknob poses you no harm, such amount of charge is actually enough to potentially damage components, rendering them useless.
In fact, anything over 10,000 volts is capable of damaging components.
Companies that work with ESDS or electrostatic discharge sensitive devices take things seriously in the workplace. We’ll talk more about this below.
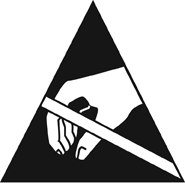
Such devices can be recognized by this symbol:
Image source here
Types of ESD Device Damage
Electronic components that are damaged by ESD is recognized as two different types of damages:
- Direct Faults
- Latent Faults
Direct Fault
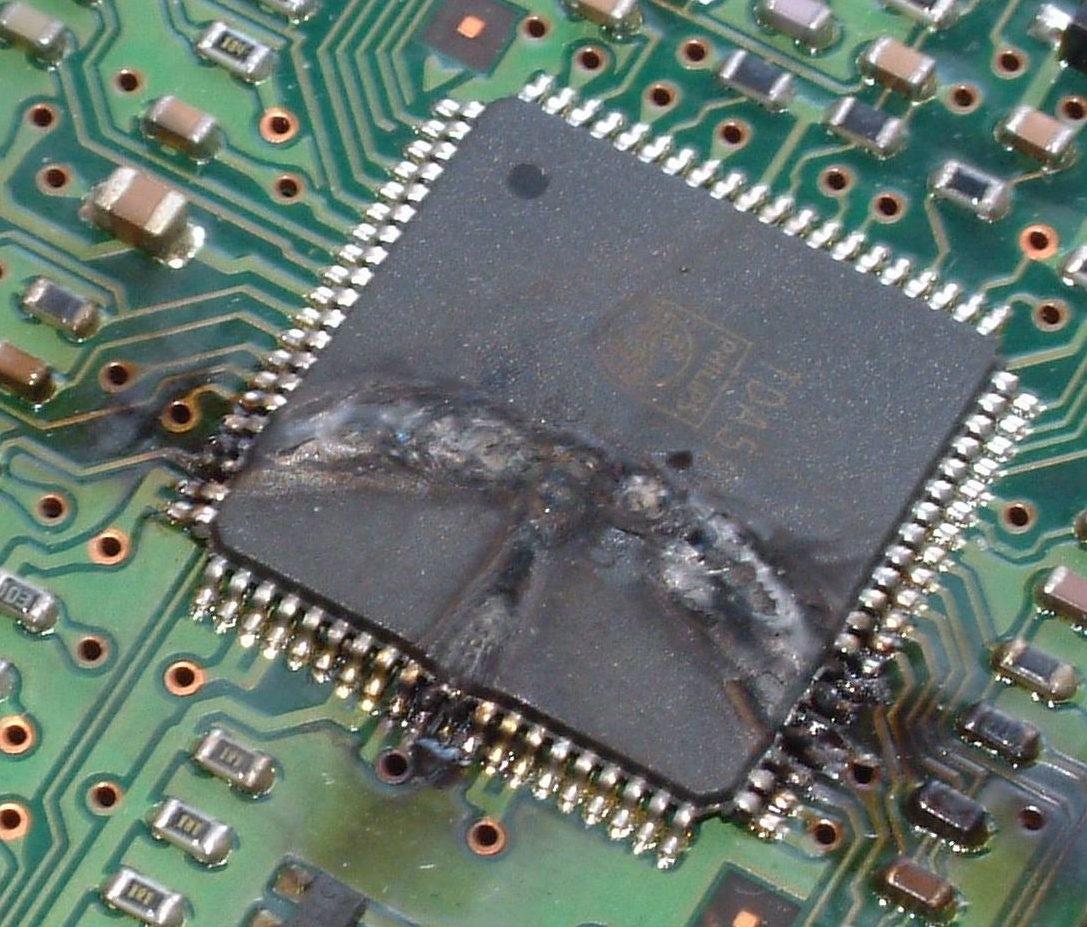
30% of ESD damages are direct faults, or also known as catastrophic failures. These are types of damages that are usually visible and what usually renders the component completely useless.
In most cases, normal inspection is enough to identify and point out direct faults.
Latent Faults
70% of ESD damages around the world are latent faults, or also known as intrinsic faults. These are not visible to the naked eye and don’t usually harm or damage the component immediately.
Most of the time, failures happen when the component is in use or in operation. When such damages kick in, severe consequences happen and may affect other components.
Reasons to Wear Anti Static Materials to Avoid ESD Damage
Companies that work around ESDS devices take precautionary measures to make sure that they work in an electrostatic discharge protected or EPA area.
This means that they can work with ESDS devices with the assurance that they don’t risk damaging it.
Computer technicians or DIY computer builders use anti-static wrist straps to make sure they don’t damage their computer hardware components.
Knowing how to properly use anti-static wrist strap is actually promoted and encouraged to make sure you don’t risk damaging any PC hardware components as you work on building one.
Many DIY computer builders and even technicians themselves don’t use anti-static wrist straps. However, it actually makes sense wearing them, especially if you’re custom building a premium gaming PC under $2000.
Such a small amount that cost under $6 goes a long way of keeping expensive computer hardware protected from ESD.
Ways to Keep Yourself from Damaging Your Components
There are a number of items you can find on the market that greatly reduces the chances of ESD.
The most effective way to avoid the risk of damaging your components is to make use of anti-static wrist straps, anti-static mats, and grounding workbench, as you work on computers and ESDS devices.
It makes sense investing in antistatic materials, especially if you work on more than one computer. But it may not be sensible to get one just so you could safely rip out the RAM from your computer for replacement.
This is why we compiled a list of ways below that can be done to help reduce the chances of damaging your hardware components with ESD.
Ground Yourself
Continuously touching bare metal parts that are grounded, or even the chassis of the computer, allows you to dissipate electrical charges you may have generated. By regularly grounding yourself, you reduce the risk of ESD.
Stand, Don’t Sit
When working on ESDS devices, it’s advisable to stand and not sit on chairs.
Compared to sitting on a chair, standing as you work on ESDS devices or your computer reduces the chances of generating negative electrical charges.
Remove Jewelry and Accessories
Don’t wear jewelry and accessories when working on computer hardware and components. Most jewelry and accessories highly conductive and it’s best to remove when everytime you work on ESDS devices and computer hardware.
Wear the Right Clothing
There are specific types of clothing that are susceptible to conduct electrical charges. A wool sweater and a synthetic fabric are known to be really good at gathering static charges.
If you want to make sure you’re wearing a safe cloth, wear clothes made of cotton.
Weather
Electrical storms are likely to increase the chances and risks of ESD or electrostatic discharge. Don’t ever think of working on computers or electrical components when there is an electrical storm.
Use Non-Static Forming Sprays
Every time you work on electrical components, computer hardware, or printed circuit boards, always check the spray and make sure they are labeled as non-static forming.
Stand on a Hard Floor in Bare Feet
Avoid working or standing on a carpet.
When working on a computer, not only that you should stand on a hard surface but it’s also recommended you stand in your bare feet.
Conclusion
Understanding the nature of how ESD works and how they damage components and computer hardware is not something everyone knows about.
The use of antistatic materials is recommended and advisable to ensure you greatly reduce the risk of damaging components and computer hardware from ESD.
By following these steps and valuing the use of anti-static materials, you greatly reduce the risks of damaging your components and hardware.