Augmented Reality for Smart City Solutions
The term smart city has been around for quite a while already, and with the 4th industrial revolution around the corner, it keeps gaining more popularity. Although there is no universally recognized definition of a smart city, its ultimate purpose is to ensure improved citizen services and a decent quality of life for urban dwellers.
However, if we dig deeper into the meaning of a smart city, it indicates comprehensive development of physical, institutional and social infrastructure to create an environment where an individual citizen can interact with the surrounding world more efficiently and effortlessly.
The first and the most fundamental step to take towards building a smart city is the application of smart solutions.
In pursuit of transforming this ambitious idea into reality, governments, urban planners, engineers and technologists join efforts to develop and leverage modern-day digital technologies like Big data, AI, IoT, and of course, augmented and virtual realities.
While all of these technologies play a crucial role in achieving a smart city success, this article focuses on augmented reality as an individual-centric solution used to promote greater independence and productivity for individual citizens. Here are three great uses of AR in smart cities.
Three uses of augmented reality in smart cities
Augmented reality is an immersive technology that superimposes digital content onto the user’s real environment. In recent years, due to the emergence of the biggest AR SDK engines, ARCore and ARKit, augmented reality has matured enough to expand its level of access and usability to the individual consumer market.
In the meantime, the emergence of high-capability smart devices and the availability of speedy network connectivity have made AR so powerful that it can contribute to making cities smart and digital in the following measures:
AR navigation
Navigators are popular for a reason: they are handy, useful and help us save time and effort while travelling to a new place. Navigation apps have become an integral part of modern smartphones and have long been used by commuters in urban cities for easier orientation.
That being said, not everybody finds it very easy to understand the directions of a navigation app just by looking at the route lines on the device screen.
Moreover, its convenience can also be questioned: to follow the directions of a navigation app, you have to constantly look at your smartphone screens and sometimes even read written instructions, which can be time-consuming, inconvenient and unsafe.
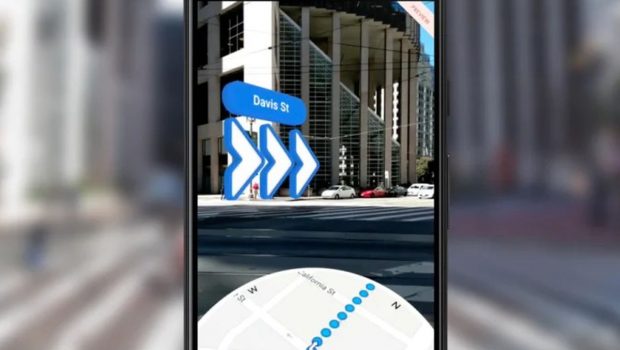
This is where AR promises greater convenience and better user experience. Instead of providing users with a complicated map, AR uses the phone camera to place information on the user’s real environment and help them navigate just by looking at easy-to-follow signs within the view of their actual location.
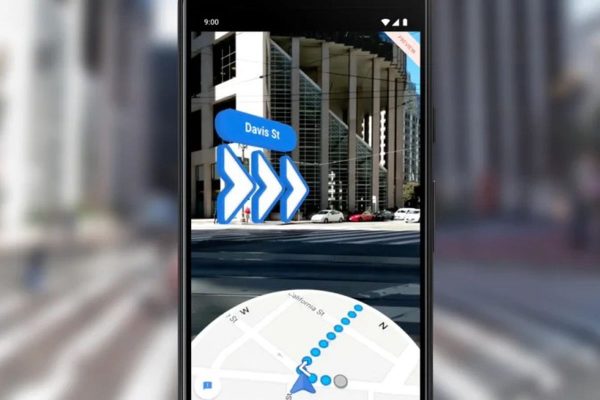
Photo credit: theverge.com
Google Maps Live View is a good example of AR navigation. It uses visual positioning, street view and machine learning to pinpoint your location.
To navigate your way with Google, you need to open the app, put your directions and hold the phone up: it recognizes the solid, stationary objects like buildings and shows what way you need to go by placing signs in your camera view.
This means that instead of looking at the map, you look at your actual street. Such an approach is not only more convenient to use but also increases safety.
AR for roadworks and highway engineering
Roadway and construction workers are the first responders when a road failure or accident occurs. They should have smooth and seamless communication, including proper information about current road conditions, structures and underground infrastructures to provide timely and appropriate solutions.
Smart cities make sure that there are appropriate measures in place once emergencies arise. For this purpose, smart cities build smart or intelligent work zones, which are a site-specific configuration of traffic control technology that provides “real-time” information, reduces the dependency on human “flaggers” and makes the work zone safer for roadway workers.
To carry out repair and maintenance operations, these specialists should be given the right tools and support. AR technology can be integrated into smart work zones to provide greater assistance and support for their needs and make roadworks safer and smarter without investing significant financial, human and other resources.
Augmented reality can be used to create platforms that store currently available data about road structures and underground infrastructures and enable roadway workers to see more than what is visible on the surface of the road.
Since more knowledge equals more protection, AR uses GIS data in the form of interactive mappings, drawings, and 3D models to provide thorough insider information about underground assets at each site, including the presence and positioning of any water pipes, power cables, gas pipelines, etc.

Photo credit: bentley.com
These non-invasive surveying features of AR also reduce health risks by allowing to considerably move away from destructive methods of determining asset locations, such as exploratory digging or potholing. This means that via their mobile device’s live video feed, workers can see and walk through interactive 3D renderings of buried assets, such as buried cables or pipes.
Imagine visiting a completely unfamiliar site, and within minutes, without digging a single hole, workers already know what assets are underground, who owns them and how they should be handled.
Interactive AR tour guides
Independent travel keeps gaining momentum. Increasingly more and more people opt to travel on their own, rather than as part of a guided group. The reason behind such a decision is that independent travel is significantly cheaper, offers more freedom and greater opportunities to immerse into local life and get the real feel of the place.
That being said, independent travel also has its drawbacks: it can often be hard to orient yourself in a new place and you might miss a lot of information about important landmarks.
Smart cities use technology to solve these kinds of problems and provide better conditions for travellers who want to explore cities on their own. Augmented reality is one of the core technologies in this regard.
One good example of how AR is used to make travelling and exploring easier in a smart city is Arloopa’s AR Guide. AR Guide is an innovative and new initiative to drive more efficient urban mobility and create greater opportunities for independent travellers in smart cities.

Photo credit: arloopa.com
AR Guide features animated 3D avatars that run virtual tours in various languages, across various locations and are available 24/7.
Locations, where AR guiding is available, are pinpointed on a dynamic map in the app. These pins become active once the user arrives at the corresponding location (due to location-based AR).
The user can then click on each pin for the virtual guide to pop up and guide their way through the city or tell about a particular landmark.
The focus is on sustainable and inclusive development, and the idea is to create a replicable model that will act as a lighthouse to other aspiring cities.







![Creating a Harry Potter Style Party [Infographic]](https://technofaq.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/harry-potter-style-party-150x150.jpg)




