The Tech Behind Microwave – How does it work?
Microwave is one of the great inventions of the 20th century. Millions of homes worldwide have a microwave. Can you imagine how many times you use a microwave every day? You use microwave when you are running late for work and there is no time to fix breakfast at home. You use microwave when you grab a frozen breakfast burrito from the quickie-mart and pop it in the microwave on the counter. You use microwave when you are starving and grab a snack-pack of microwaveable popcorn from the vending machine and pop that in the break-room microwave. You use microwave when you dish up last night’s lasagna and heat it up in.
By considering all the above microwave uses, you can see that microwave ovens are becoming very popular because they cook food in an amazingly short amount of time. Consider the Convection Microwave Reviews because such microwaves have many advantages over standard microwaves.
This page discusses the mystery behind the magic of “meals in a minute” with microwave cooking.
How microwave works?
Microwave is a remarkable gadget that can cook food quickly without any visible source of heat. They usually work on the basis of radiation waves. Generally, microwave ovens generate waves of radiation that penetrate your food. It works on its water molecules and makes them bristle with energy. As a result of this, the water molecules begin moving faster and faster. They begin to knock into each other more and more. This whole process translates to hotter water inside increasingly hot food.
1. Microwave cooks food by injecting electromagnetic waves
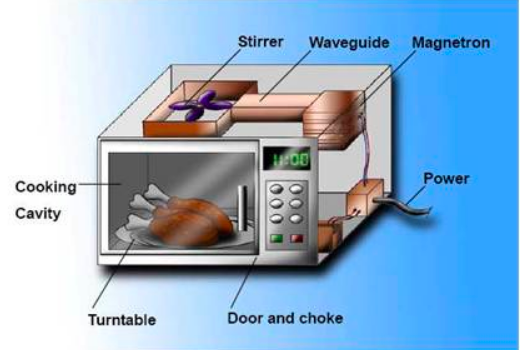
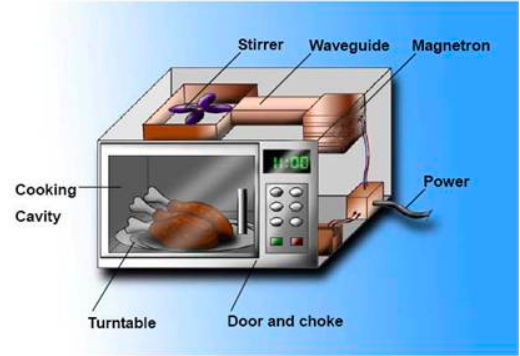
You will be surprised to know that microwave cooks food by injecting them with surprise microwaves. These microwaves are in fact a form of energy. They are invisible to the human eye and fall between radio waves. There is a device called magnetron that is present inside the guts of a microwave. It channels electrical energy from a power outlet to a heated filament. In this way, it creates a flow of electrons that in turn transmits microwaves into the cooking chamber through an antenna.
2. Microwave works through radiation heating
The electromagnetic waves in a microwave bounce around in the chamber and cook food through radiation heating. Usually, the outsides of thicker foods become heated by microwaves. This is because the microwaves can travel so far before losing momentum. Moreover, with this, the insides of the food are heated subsequently by the conductive transfer of heat from the outsides.
For example, just consider that you want to bake a cake in a conventional oven. Normally a cake is baked at 350 degrees F (177 degrees C). But accidentally, you set the microwave oven at 600 degrees F (316 degrees C) instead of 350. Now, what will happen? You will be surprised to know that the outside of the cake will burn before the inside even gets warm. The fact behind this is, in a conventional oven, the heat has to migrate from the outside of the food towards the middle by the process of conduction. The outside of food becomes crispy and brown while the inside remains moist. At this point, the radio waves start penetrating the food and excite water. Hence, the whole heating process works by exciting the atoms.
3. Microwave oven produce microwaves
Microwave ovens work by following a quite simple process. Like any other household gadget, it also takes in electrical energy. It then passes this electrical energy to a cavity magnetron. It is considered as the most important device in the production of microwaves. After that, these radiations go through a waveguide, through which the waves are directed into the cooking chamber.
Conclusion
All the above points will definitely help you to explore the science behind the working of microwaves!