There was a time when the human-computer interactions were limited to the use of keyboards and mouse. Though a majority of the users still rely on the mouse-keyword union to interact with the computer, the introduction of touchscreens has provided us with an alternative which is more accurate and more convenient. But what is next? Will it be possible to instruct the computer without any direct contact, with nothing but a combination of voice and gesture?

The answer is yes. Interestingly, we already have a device that can revolutionize the way we humans interact with our computers. Leap Motion is the first successful product in the mainstream market that the users you to manipulate digital objects on their computers just with the hand gestures. In fact, the Leap Motion Controller device tracks the movement of your hands within eight cubic feet of space with impressive speed and accuracy.
Why is Leap Motion so significant?
As said, up until now, almost every interaction with the computer program required an intermediary between the human hand and the digital environment. Leap motion tries to bridge the gap by allowing the users to manipulate computer programs just like they manipulate objects in the real world.
How does Leap Motion work?
Leap Motion did not just appear out of nowhere. There has been a lot of development revolving the Leap Motion platform in the past few years. To understand how this device works, you need to learn a few things about its hardware as well as the software.
-
Hardware:
The hardware part in the Leap Motion Controller is actually quite simple to understand. It consists of two cameras and three infrared LEDs. These components allow the device to track infrared light (with a wavelength of 850 nanometers) that is outside the visible light spectrum.
Source here
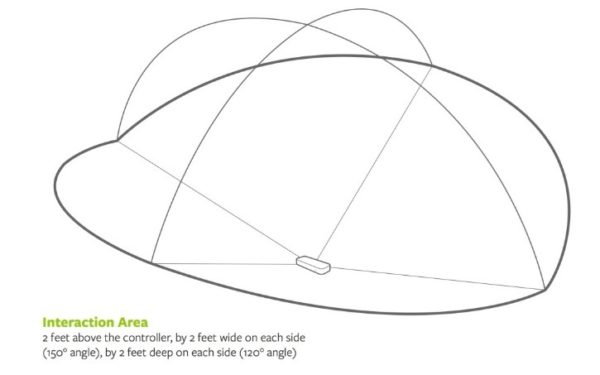
The wide angle lenses in the device allow the Leap Motion controller to function at a large interaction space of eight cubic feet. The interaction area looks something like an inverted pyramid as mentioned in the picture above. Earlier, the viewing range of the Leap Motion controller used to be 2 feet (60 cm) above the device. Thanks to the Orion beta software, the range has been expanded to 2.6 feet (80 cm).
Interestingly, the range of the controller is limited by the LED light propagation through space as it becomes harder for the device to infer the user’s hand’s position in 3D beyond a certain distance. Also, the LED light intensity is limited by the maximum current that can be drawn over the USB connectivity.
Currently, the USB controller of the device reads the sensor data into its very own local memory and then performs the necessary resolution modifications. The Leap Motion tracking software then streams the data via USB. The data finally takes the form of a grayscale stereo image of the nearby infrared light spectrum, separated into the right and left cameras.
If you are using the device, you will only get to see the objects which are directly illuminated by the controller’s LEDs. Though, halogens, incandescent light bulbs and daylight will also light up the scene in infrared.
-
Software:
After the image data is streamed to the computer, the system does some heavy mathematical lifting. Surprisingly, the controller does not generate a depth map. Instead, it uses an advanced algorithm to process the raw sensor data.
After the compensating for the background objects and ambient environmental lighting, the images are then analyzed to construct a 3D representation of what the device sees. After that, the tracking layer matches the data to collect tracking information such as the fingers and tools. The Leap Motion’s website, the tracking algorithms interpret the 3D data and deduce the positions of nearby objects. The software uses filtering techniques to ensure there’s smooth temporal coherence in the data. It then feeds the results into a transport protocol in the form of a series of frames or snapshots which contain all of the tracking data.
The protocol further allows the software (Leap Motion Service) to communicate with the Leap Motion Control panel. The software even communicates to the native and web client libraries through a local socket connection (TCP for native and WebSocket for Web). It is the client library that organizes the data into an object-oriented API structure while managing frame-history and providing the helper functions and classes. At this point, the application logic ties into the Leap Motion input, which further amplifies the motion-controlled interactive experience.
The real world use of the Leap Motion Controller
The initial use of the Leap Motion device shows quite satisfactory results when it is stationary and not kept near a bright source of light. You can run an application or play a game with the Leap Motion device after attaching it to the laptop. However, if you are moving around, the game or application may get interrupted as the varying light sources can make the device lose track of the hand.
Also, the Leap Motion controller only works with programs that are specifically written for it. So for now, the use of Leap Motion is strictly restricted to the programs that are built with the controller in mind. Even though most software run quite well on the device, it has a tendency to be inconsistent.
Can Leap Motion be used in higher education?
Since the Leap motion controller allows the user to manipulate 3D objects in an instinctual way, it can be used to get students familiarized with complex structures. Currently, the chemistry students can examine the molecules from the RCSB protein bank using the Molecules program, and the anatomy students can use software like Cyber Science 3D to dissect a body using Leap Motion.
It can also provide the structural engineering students with significant assignment help on various projects if there’s a proper application in place. So, if more applications can be created keeping the functionality of Leap Motion in mind, the education sector can get benefited quite significantly with gesture-based computing.
Where is this leading to?
Currently, the Leap Motion controller can do very little as the application of the device is limited to a handful of applications and games right now. However, it has the potential to become something incredible as there’s a lot of scopes for the developers to design their own software which can leverage the creative potential of the Leap Motion controller.
As mentioned previously, it is only the beginning of sophisticated gesture control of computers. And in a short period, Leap Motion has proven its worth to the people who are willing to take the human-computer interaction to another level. And since it is a revolutionary product, it won’t be a surprise anymore, only if the PC manufacturers start building the Leap Motion devices directly into the laptops and desktops.
Author bio: Gracie Anderson is an IT Assignment expert who is currently employed at one of the major IT firms in Australia. She has also been associated with MyAssignmenthelp where she provides students with necessary assignment help on IT-related issues.


