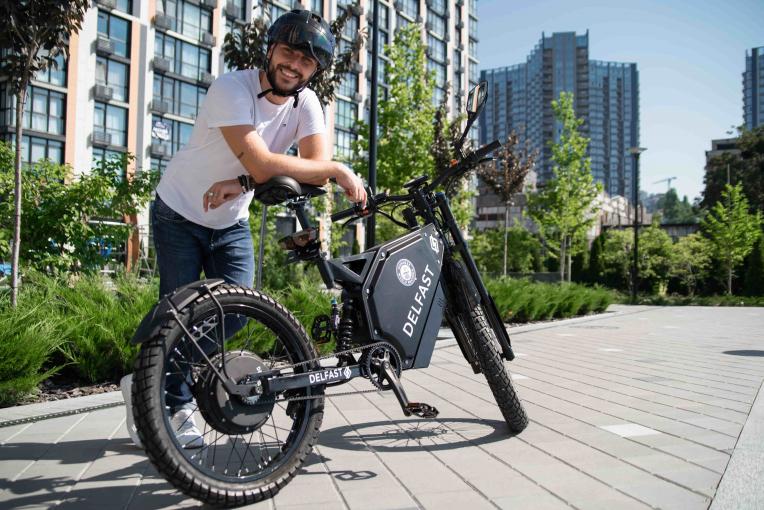
Global warming is a reality. Greenhouse emissions are greatly responsible for this phenomenon. Is there a way to reverse it? Yes, we all can do something to save our planet. For example, you can reduce your driving and use an electric bike instead. Electric bikes don’t burn any fossil fuels. Therefore, such vehicles can help you reduce your carbon footprint. If you are serious about contributing to counter climate change, try riding an environmentally-friendly e-bike like the Delfast TOP 3.0.

The Importance of a Good Battery
Instead of burning fuels, electric bikes are powered by an electric motor. For its part, the said motor is powered by a battery. As such, the battery is one of the most important components of an electric bicycle. Although a battery increases the weight of an ebike significantly, choosing the right type of battery can yield the best weight-capacity tradeoff.
The capacity of a battery refers to the amount of electric power it can provide without being recharged. The higher the battery capacity, the better. There are many different types of batteries in the market: Nickel-Cadmium, Silver-Zinc, Lead-acid, Lithium-ion, and more. However, not all of them fit the needs of an electric bike. Let’s take a look at some of the batteries that are used to power these two-wheeled vehicles:
- Lead-Acid (Gel) Batteries. This type of battery is used less frequently for electric bikes because of its several drawbacks. A gel battery is usually very heavy and has very low capacity. It takes between 8 and10 hours to fully charge it. Also, the life of a gel battery is short (150-200 cycles).
- Lithium Polymer (Li-Po) Batteries. This type of battery has been used in electric cars successfully. They have a better capacity than gel batteries. They also have a longer life. LiFePo4 Battery is a good brand to consider for these batteries. However, they are not resistant to impact and vibrations. Therefore, they are not suitable for all types of electric bikes. They are also prone to ignition if the BMS fails or in the case of a short circuit.
- Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Batteries. This type of battery is ideal for electric bicycles. A Li-ion battery offers the best tradeoff between weight and capacity. Compared to other types of batteries, Li-ion batteries have the greatest capacity and longer life. Their drawback is their sensitivity to temperature changes, which alter their performance.
- Lithium Iron Fosfate (LiFePO4) Batteries. These batteries are a new variation of the Li-ion type. They are already popular in different applications. Little by little, they are being adopted in the e-bike industry. In comparison to Li-ion batteries, they offer some advantages. For example, they can work in extremely low temperatures (up to -30 °C) without losing capacity. Also, they have a longer life. However, they are still too expensive.
Main Parameters of Every e-Powered Device
Now that you know the different types of e-bike batteries, you can choose the most convenient for you. In general, the battery should match the electric requirements of the electric motor on your e-bike. The following parameters characterize the motor: Volts, Amps, and Watts. The first parameter refers to the voltage or electric potential that is applied to the terminals of the electric motor. Amps are a measurement of the electric current flowing through the electric circuit of your e-bike. Watts indicates the electric power that the motor consumes while you ride.
As said, the battery should match the above parameters. For example, if the electric motor is labeled as 48V, the battery should supply 48 Volts. However, the previous parameters alone don’t characterize the performance of a battery. Therefore, a couple of additional parameters is commonly used to characterize a battery. Amp-Hours (Ah) is a better way of characterizing a battery. This parameter indicates the number of Amps that a battery can sustain during 1 hour. Alternatively, one can use Watt-Hours (Wh), which indicates the amount of usable energy per hour. Both parameters are measurements of the capacity of the battery.