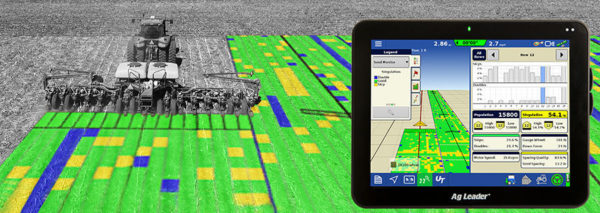
There is no doubt that automation has revolutionized the food industry. Most farmers have embraced them to produce more quality food supplies. With the increasing demand of food, automation is the only solution. Otherwise you won’t meet the demand caused by calamities, global warming etc.
Gone are the days when farmers had to practice physical farming. In the long run it is expensive in terms of money, time spent and less production. That’s why technology invented collaborative robots that produce more at less costs. However, there are many types of industrial robots on sale. Not all will do the work as you deserve. So take extra caution before you get excited by the benefits of automation and just buy any brand available.
Universal Robot’s automation will handle all your farming applications. Let’s explore more in this article.
Nursery Planting
It is one of the first steps in the food production line. Here, seeds are grown into seedlings. These can later be transported to the actual farm or sold to other farmers. At this stage, you need quality seeds that will ultimately lead to better nursery plants. With more people embracing farming, nursery plants are on high demand and hence call for nursery automation. That’s why companies like Harvest Automation and HETO Agrotechnics give automation advice for seeding, potting and warehousing of plants in greenhouses.
Seeding Process
Gone are the days when people were using tractors in the seeding process. Traditionally, farmers were using the “broadcast spreader” attached onto a tractor to sow seeds. Its efficiency depends on the tractor’s speed. If it’s driving very fast, lots of seeds are scattered leading to wastage. On the other hand, Autonomous precision seeding is a more efficient method since it combines geomapping and robotics. It studies the soil properties like density and quality at every point and creates a map of the field. Then a tractor with an attached seeding attachment puts seeds at precise depths and locations. Each seed stands a chance of growing because there is no chance of overcrowding.
Irrigation
Traditionally, irrigation was considered an expensive procedure because it required too much water. As a result, it was found to be less efficient. However, Robot-Assisted Precision Irrigation targets specific plants thus being more efficient. Ground robots independently move between rows of crops and deliver water directly at each plant. Therefore chances of error and wastage are minimized.
Fertilization
Fertilization is expensive, so when you are fertilizing a vast land, you want to minimize wastage. This can only be achieved by automation. Robots stand a higher chance of accuracy as they can access areas that other machines cannot. For instance corn growers find it hard to efficiently fertilize them since they grow very fast. Therefore Rowbot was invented to provide a solution to this problem. It easily moves through corn rows and delivers nitrogen fertilizer to the base of each corn plant.
Monitoring and Analysis
Monitoring a huge piece of land can be a daunting process. To counter this, farmers have embraced use of drones and ground robots. They are fitted with hardware and analysis software that help farmers with data to monitor their fields. For example, a farmer takes the drone to the field and programs the software via a phone or tablet. Then he can view the needed crop data as it happens. BoniRob Robots are even more accurate monitoring since they get much closer to the plants.
Spraying and Weeding
Pesticides can be harmful to crops, people and the environment. Therefore spraying of insecticide should be done with caution. Therefore, it’s advisable to use robots which reduce wastage and reduce chances of error. Micro-spraying robots such as AG BOT II utilize computer vision technology to identify weeds. After, it sprays a targeted amount of herbicide onto the targeted weeds.
Harvesting
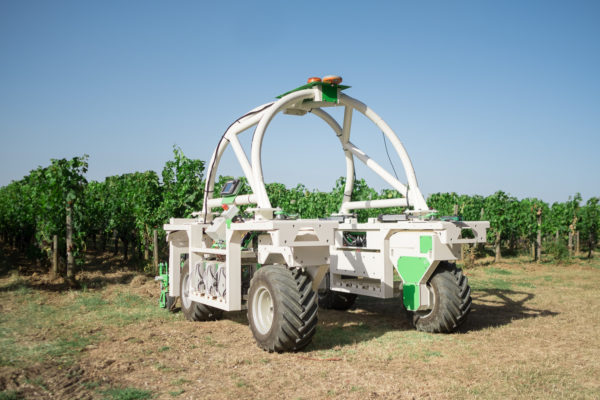
Some crops can be simple to harvest. They include wheat, corn barley etc. therefore, they can be harvested using an automated combine harvester. However, the more difficult crops to harvest like soft fruits require manual dexterity. Even with these more harvesting application projects are ongoing to harvest crops like grapes and sweet pepper.
Conclusion
Automation has changed the dynamics of agriculture. Most farmers have embraced it because it reduces wastage, error and damage. Most machines are big and thefore cannot access each crop. Automation uses small drones and robots that can access each plant and perfom the task effectively.