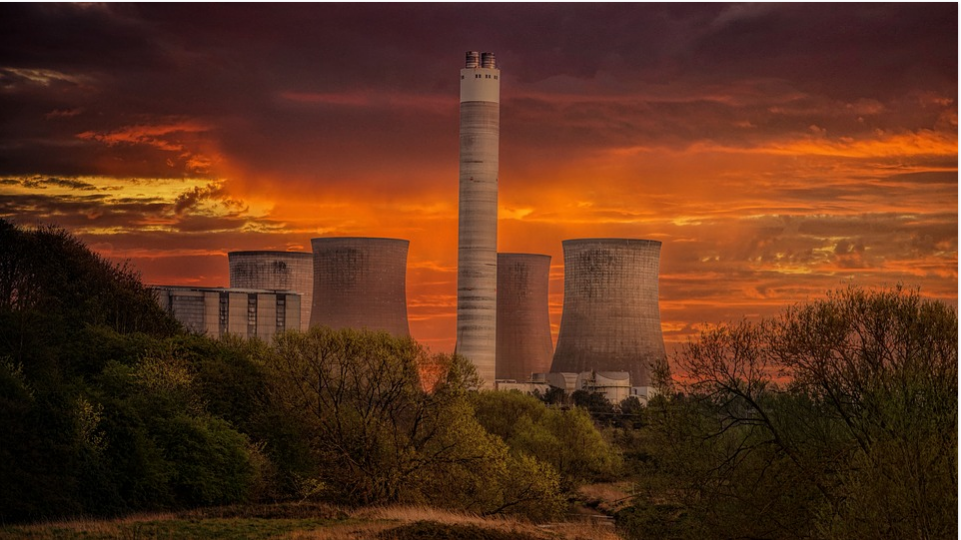
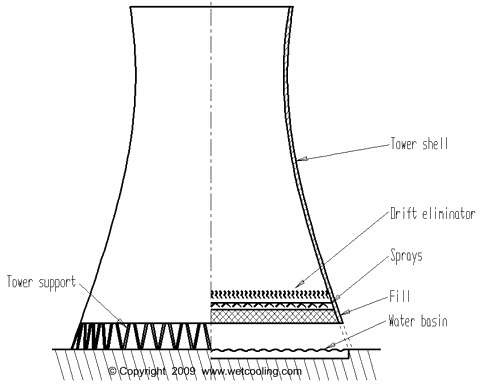
There is a lot of heat generated by industrial processes and machines, which if not dealt with, could cause massive damage to the environment. It is for this exact reason that the cooling tower was developed.
Cooling towers help in the continuous dissipation of heat in industries where there is a large amount of heat produced, thus improving efficiency. They help eliminate excess heat which is expelled into the surrounding biosphere.
There are a lot of methods for achieving this, but cooling towers are very efficient in this regard and thus the various types of cooling towers that we see today. Ideally, each of these cooling towers have different working processes and working principles.
However, the end results of each of these processes are the same.
Generally, the different types of cooling towers get their names according to how air or water flows in them during the cooling process. It is for this reason, that you will have names such as counterflow, crossflow and hyperbolic systems in different types of cooling towers.
Additionally, there are other two which are classified solely on the flow of air and these are the passive draft and induced draft cooling towers. There is also the natural draft and the mechanical draft cooling tower.
Each of these types of cooling towers performs their work in different ways and under different technologies but all eventually help cool the water.
Read on to find more information about each of these cooling towers available in the market today. This information will also help you make concrete decisions on the type of cooling towers that you should invest on when looking forward to providing efficient operations of the machines in your industries and cooling plant.
Category by Air to Water Flow
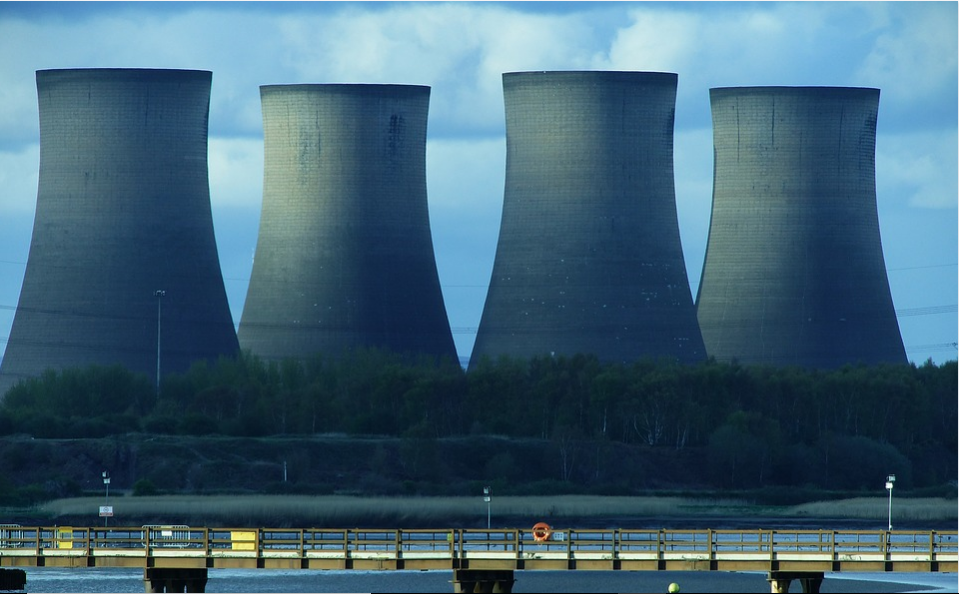

Cross Flow Cooling Towers
This is a type of cooling tower that uses a splash fill that gives a chance to the in-flowing air to move in a horizontal path over the stream of water from the upper reservoirs. Despite crossflow cooling towers being the most expensive to purchase, they are among the cheapest to and easiest to maintain.
However, unlike other cooling towers, crossflow cooling towers are more vulnerable to frost.
In these towers, air flows horizontally through the cooling tower’s structure, as hot water flows downwards from the distribution basins. They can be as tall as other cooling towers such as counterflow towers but are also more prone to freezing, thus making less efficient as compared to other cooling towers available in the market.
Applications of Cross Flow Towers
- Used in the heating process in the chemical industry
- Used in illumining die casting and air compressor
Advantages of Cross Over Towers
- Low energy consumption
- Have minimum maintenance
- Low operation cost due to low pumping head
Counterflow cooling tower

In this kind of cooling tower, the in-flowing air travels in a vertical path over the splash fill as the water streams down from the reservoir above. You will realize that the counterflow systems will be smaller as compared to that in the crossflow counterparts.
Counterflow cooling towers are also more expensive since energy is needed to help push the air being cooled upwards against the down falling water. It is, therefore, good to note that the counter flow towers move the air upwards through the tower while water flows downwards to cool the air.
The counterflow cooling towers are more often than not compact in footprint as compared to the crossflow towers, thus saving more energy overall.
Applications of counterflow cooling towers
- Refineries and natural gas processing plants
Advantages of counterflow cooling towers
- Has the maximum tower performance of its kind
- More efficient to air to water contact due to droplet distribution
Disadvantages of counterflow cooling towers
- Uneasy maintenance and difficult to clean up
- More noise production due to spraying and falling water
Hyperbolic cooling towers
These are well-built cooling towers that require minimum amount of resources. These towers are built with few resources and are able to efficiently manage large-scale tasks that are found in big chemical and power plants.
The hyperbolic cooling towers use chimney stalking techniques which helps the outside air and cooler to push the damp, thus warming the air inside the tower. Splash fill is then placed at the bottom of the tower and the water that sprays over it is cooled by the passage of upward-flowing air.
Fill in the hyperbolic cooling towers is placed around the lower portion of the tower, where water is later sprayed and cooled by the natural draft of water that is moving up through the tower.
Category by Drawing Air Through the Tower
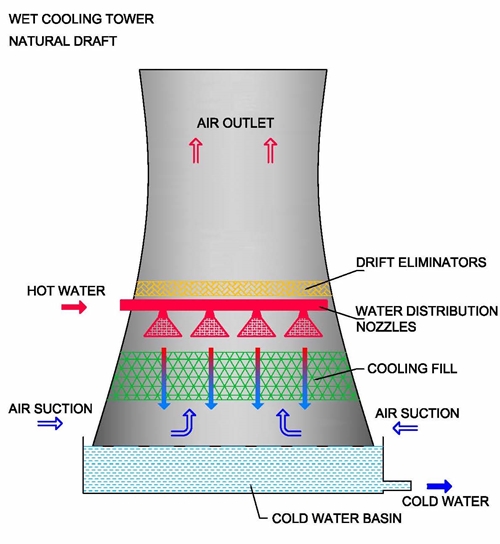
Natural Draft Cooling Tower
This cooling tower system works by removing waste from the system and release it into the atmosphere. During this process, there is hot air that enters through the series of pumps to the top area of the tower, near the hot water inlet.
There is also a series of cooling tower nozzles that are connected to the hot water inlet and are used to spray water over the cooling tower fill and distributed throughout the tower. Air is then simultaneously introduced to the bottom of the tower while flowing in an upward direction.
Later on, it is circulated inside the cooling tower by natural convection. This is done as flowing water emits heat due to evaporation, which later mixes with the air that is flowing upwards making it cool down.
The water that has cooled is then collected into a basin and used for cooling various hot process fluid.
Applications
- Used in power stations and for process cooling applications
Advantages
- Safe to operate
- It is energy efficient
- Less operating and maintenance costs
Disadvantages
- High initial coat
- Requires a large space to install
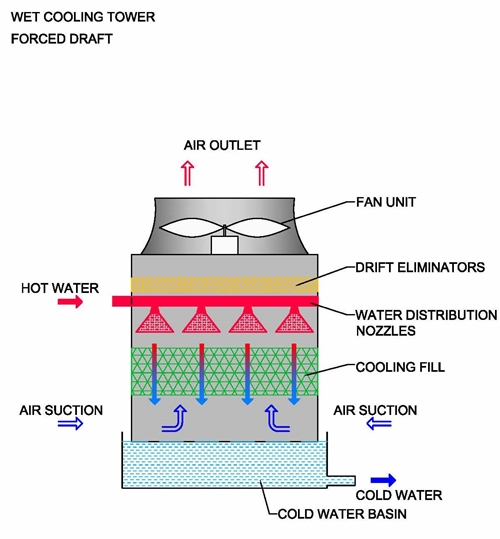
Mechanical draft cooling tower
This is a cooling tower that uses mechanical devices to perform its functions. Some of these devices are such as fans and blowers which help in moving air through the tower.
Mechanical draft coolers are classified into two namely
Induced draft cooling tower- air is introduced from the bottom of the tower and enters from the top. Water then gets spread throughout the tower with the help of the distribution header.
Forced draft cooler- air is blown through the tower with the help of a fan located at the bottom of the tower. This type of tower removes low potential heat generated during the production process a having limited application due to recirculation difficulties.
Conclusion
There are various types of cooling towers, all classified under different categories. For this reason, when looking forward to investing in a cooling tower, be careful to consider all the available options in the market and pick that which suits you the best.